Low volume injection molding service
We provide low volume injection molding with design and engineering support, competitive price, mold making, OEM, ODM, high quality bulk, shipment support etc
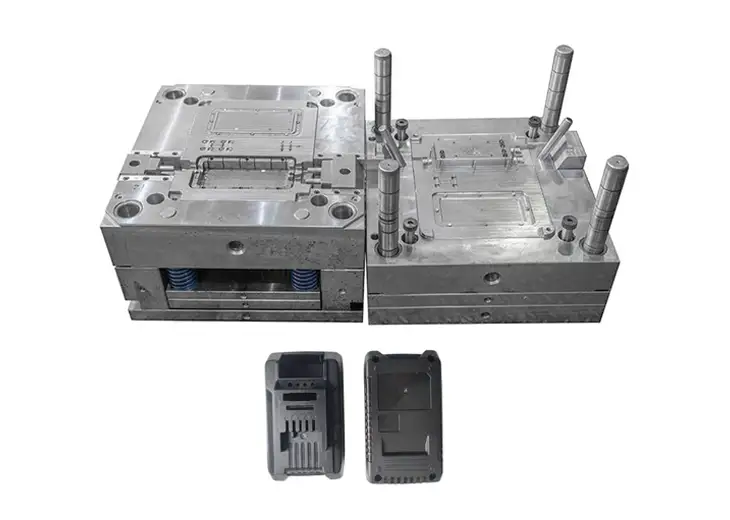

Low volume injection molding has become a critical manufacturing solution for companies that need high-quality plastic injection-molded parts without committing to mass production. For many molding projects that involve low volumes, short-run requirements, or early-stage product validation, this manufacturing method offers an ideal balance between cost, speed, and production accuracy.
Whether you are launching a new product, developing a plastic prototype, validating a mold design, or supplying niche markets, low-volume injection molding provides a cost-effective injection molding solution. It bridges the gap between prototype injection and high-volume production, making it especially valuable for startups, engineers, and product teams that need flexibility without sacrificing part quality.
In this guide to low-volume injection molding, we’ll explore what low-volume injection molding is, how the injection molding process works, its benefits, applications, materials, tooling strategies, cost considerations, and how to choose the right plastic injection molding services or injection molders for your project.
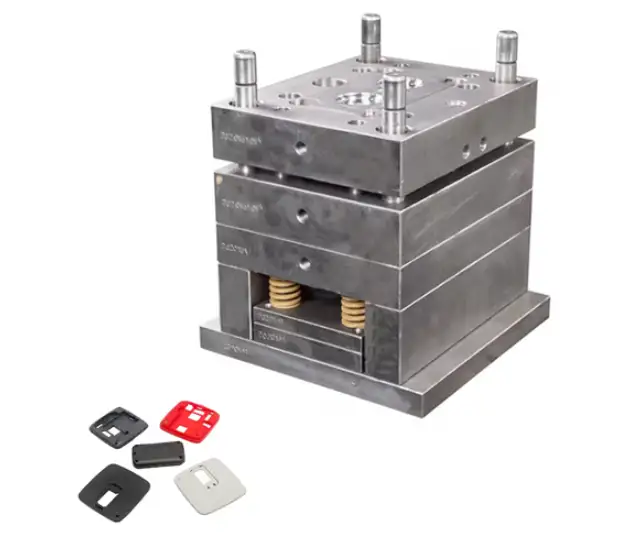

What Is Low Volume Injection Molding?
Low volume injection molding refers to the production of plastic parts in small to medium quantities, typically ranging from 50 to 10,000 injection molded parts, depending on the tooling approach, mold material, and minimum order requirements.
Unlike traditional injection molding, optimized for high-volume or mass production, low-volume injection molding focuses on efficiency for low-volume manufacturing. It emphasizes:
Reduced injection mold and mold tooling costs
Faster lead times compared to high-volume tooling
Greater design flexibility for prototype injection molding
Small batch injection molding and short-run production
This approach is widely used in prototype injection mold development, bridge injection molding, pilot production, and short-run manufacturing where market demand does not justify the total cost of hardened steel tooling.
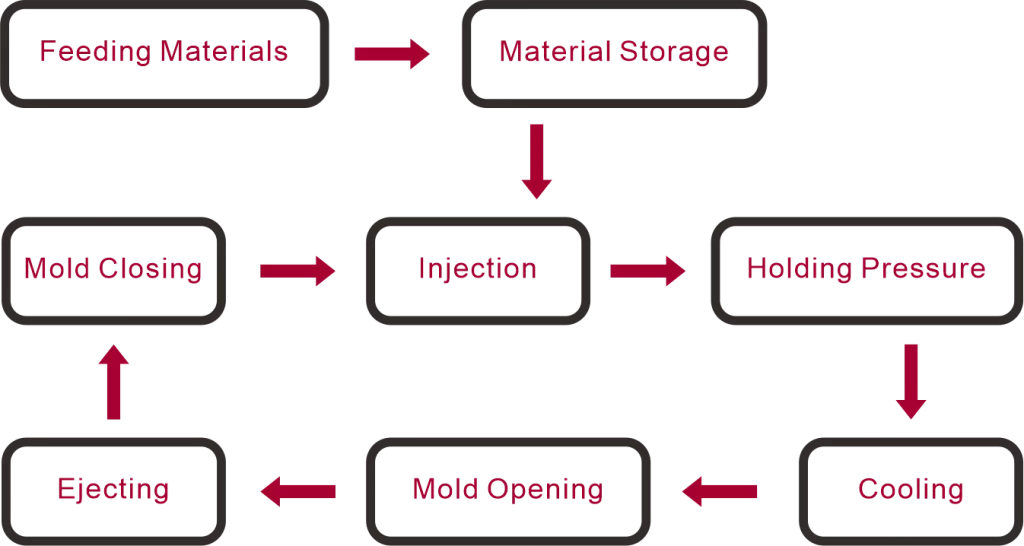
How Low Volume Injection Molding Works
The core injection molding process used in low-volume production is fundamentally the same as plastic injection molding used in mass production. However, it is optimized for shorter production cycles, lower tooling investment, and faster iteration.
Step 1: Part Design and DFM Analysis
The process begins with a CAD model of the plastic part. Experienced injection molders perform Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis to ensure the part is suitable for low-volume plastic molding.
Key considerations include:
Optimizing wall thickness to ensure proper material flow
Reducing undercuts to simplify mold design
Minimizing material waste during the injection molding process
Improving mold life for aluminum mold injection molding or soft tooling injection molding
This step is essential for controlling cost, ensuring consistent quality, and extending mold usability across multiple short-run molding projects.
Step 2: Tooling Fabrication
Low volume injection molding typically relies on low-volume tooling rather than hardened steel molds used for high-volume production. Common tooling options include:
Aluminum injection mold tooling
Pre-hardened steel molds
Hybrid mold bases combined with prototype inserts
Compared to traditional injection molding tools, these molds are faster and cheaper to produce, allowing manufacturers to iterate on designs quickly. For some early-stage projects, 3D printed inserts may also be used for very low volumes or proof-of-concept runs.
Step 3: Injection Molding Production
Once tooling is complete, molten plastic material is injected into the mold cavity using an injection molding machine. The material is then cooled and ejected to form finished plastic injection molded parts.
During low-volume injection molding, parameters such as injection pressure, melt temperature, cooling time, and cycle speed are carefully adjusted to match the mold material and production goals. This ensures consistent results even in short-run or small-batch injection molding scenarios.
Step 4: Post-Processing and Quality Control
After molding, plastic parts may undergo secondary operations to meet final application requirements. These can include:
Trimming and deflashing
Surface finishing or texture matching
Assembly or insert installation
Dimensional inspection and functional testing
Quality control is especially important in low-volume plastic production, as parts are often used for functional testing, pilot programs, or direct end-use applications.
Key Benefits of Low Volume Injection Molding
The benefits of low-volume injection molding make it an attractive option for manufacturers across many industries, particularly when flexibility and speed matter more than sheer output volume.
1. Lower Tooling Costs
One of the primary benefits of low volume injection is the reduced upfront investment. Aluminum mold injection molding and soft tooling injection molding significantly lower injection mold costs compared to hardened steel tools used in high-volume production.
This makes low-volume injection molding ideal for startups, R&D teams, and companies managing cost-sensitive projects.
2. Faster Time to Market
Low-volume tooling can often be completed in weeks rather than months. This allows companies to:
Launch products faster
Respond quickly to customer or market feedback
Iterate designs without incurring excessive tooling costs
For short-run and prototype injection molding, speed is often a competitive advantage.
3. Design Flexibility
Because low-volume molds are easier to modify, design changes can be implemented quickly. If wall thickness adjustments, feature updates, or functional improvements are required, modifying an aluminum mold is far more practical than reworking hardened steel tooling used for mass production.
4. Production-Grade Part Quality
Unlike 3D printed or cast prototypes, low-volume injection molding produces real injection molded parts with the same material properties found in high-volume plastic injection molding.
This includes:
Consistent mechanical performance
Tight tolerances
High-quality surface finishes
As a result, parts produced through prototype injection molding or short-run injection molding are suitable for functional testing and real-world use.
5. Bridge Manufacturing Solution
Low-volume injection molding is frequently used as a bridge between prototype injection molding and full-scale mass production. It allows companies to supply the market while high-volume tooling is still being developed, reducing risk and improving cash flow.
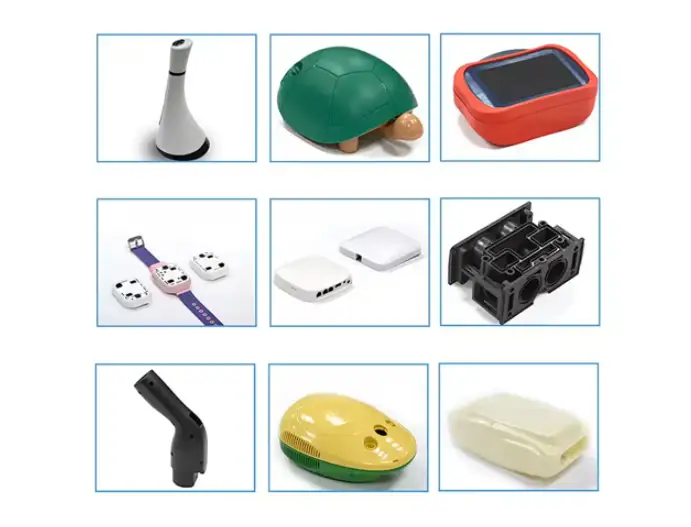

Common Applications of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low-volume injection molding is widely used across many industries where low-volume production, fast turnaround, and tight tolerances are required. Injection molding is used when companies need production-grade plastic parts without committing to full volume manufacturing or mass production.
These injection molding methods provide lower costs and higher accuracy compared to other rapid prototypes or plastic prototyping services.
Because injection molding provides repeatability and consistency, it is ideal for small batch and short production runs across a wide range of injection molding projects.
Product Development and Prototyping
Companies use low volume injection molding for injection molding for product development, allowing them to produce parts that closely match final volume production components. This prototype-to-production molding approach supports rapid design validation and DFM optimization.
Functional prototype injection molding parts accurately represent final products in terms of:
Strength using engineering-grade plastic parts
Appearance and surface finish
Performance under real-world conditions
Compared to 3D printed parts, injection molding services allow teams to run plastic injection molding with real thermoplastic materials, making it easier to iterate designs before scaling to volume production.
Medical Devices
Medical manufacturers rely on low volume injection molding solutions for regulated, low-volume production environments. Injection molding provides consistent quality during pilot production injection molding, and clinical validation stages.
Common applications include:
Diagnostic device housings
Surgical tool components
Disposable medical products
Using controlled molding processes, molten material is injected into precision mold cavities and ejected using ejector pins to maintain tight tolerances. This supports regulatory testing and controlled production runs before full-scale volume manufacturing begins.
Automotive Industry
Injection molding is used in the automotive industry for small-run plastic parts where demand does not justify high-volume tooling costs.
Typical automotive injection molding projects include:
Interior trim components
Custom brackets and clips
Low-demand replacement parts
Low volume production is ideal for specialty vehicles, aftermarket components, and limited-edition models. Aluminum mold tooling and soft steel molds help control production costs while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Consumer Electronics
Low volume injection molding supports on-demand injection molding for fast-moving consumer electronics markets, where short lead-time injection molding is critical.
Applications include:
Pilot runs for new devices
Enclosures and housings
Internal structural components
Injection molding machines equipped for low MOQ injection molding enable manufacturers to respond quickly to market changes while maintaining consistent quality across small batch production runs.
Industrial Equipment
Manufacturers of industrial equipment rely on custom thermoplastic molding for durable, functional components used in demanding environments.
Low volume injection molding is used to produce parts such as:
Machine covers
Custom fittings
Replacement or legacy parts
Injection molding services support ongoing low-volume manufacturing solutions for equipment that requires long-term support but limited annual volume.
Startups and New Product Launches
Startups benefit from low-volume injection molding by reducing risk, tooling costs, and upfront capital requirements. Rapid tooling services combined with short lead times allow startups to validate designs, test markets, and move from prototype to production molding without committing to full volume production too early.
Materials Used in Low-Volume Injection Molding
One of the major advantages of low-volume injection molding is access to production-grade thermoplastic materials rather than prototype-only plastics.
Common Thermoplastic Materials
ABS – Durable, impact-resistant, easy to process using standard molding machines
Polypropylene (PP) – Lightweight, chemical-resistant, suitable for small batch production
Polycarbonate (PC) – High strength, transparency, and dimensional stability
Nylon (PA) – Excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance
PEEK – High-temperature and chemical resistance for demanding applications
TPU / TPE – Flexible and elastic components for functional assemblies
These thermoplastics behave consistently during the molding process, ensuring predictable results across low-volume production runs.
Material Selection Considerations
When selecting a mold material and plastic material combination, manufacturers evaluate factors such as:
Mechanical and structural requirements
Heat and chemical resistance
Regulatory and industry compliance
Production costs and total cost per part
Compatibility with the injection molding machine
Proper material selection ensures a stable flow of molten material, reduced scrap, and consistent quality throughout the injection molding project.
Tooling Options for Low Volume Injection Molding
Tooling strategy directly affects tooling costs, turnaround time, and part quality in low-volume injection molding.
Aluminum Injection Molds
Aluminum molds are the most widely used tool type for low-volume injection molding due to their balance of speed and cost.
Advantages include:
Lower tooling costs compared to steel tools
Fast mold manufacturing using CNC machining
Excellent thermal conductivity for shorter cycle times
Limitations include reduced mold life and limited suitability for highly abrasive thermoplastics. However, aluminum mold tooling remains ideal for pilot production injection molding, and short production runs.
Soft Steel Molds
Soft steel molds offer increased durability compared to aluminum while remaining more affordable than hardened steel tools used in volume production.
They are suitable for medium production runs, tighter tolerances, and more demanding injection molding methods where part geometry or material requires added tool strength.
Modular and Hybrid Tooling
Some injection molders use modular mold bases with interchangeable inserts. This approach allows multiple injection molding projects to share the same base tool, reducing tooling costs and improving flexibility for low-volume production.
Hybrid tooling solutions support rapid design changes, faster turnaround, and efficient scaling from small batch injection molding to volume manufacturing when demand increases.

Cost Factors in Low Volume Injection Molding
Understanding the cost structure of low-volume injection molding helps manufacturers plan production needs, control budgets, and choose the most cost-effective manufacturing process for low quantities or small run production.
Low-volume injection molding provides a cost-effective way to produce plastic parts when full-scale volume production is not required, especially for complex parts or parts with tight tolerances.
Tooling Cost
Tooling cost is often the largest upfront expense in an injection molding project. It depends on several factors, including:
Part complexity and geometry
Number of cavities in the mold cavity
Mold material selection
Surface finish and tolerance requirements
Low cost mold tooling, such as aluminum molds or soft steel tools, is commonly used for low-volume injection molding. These tools are created through custom injection mold fabrication, often using CNC machining based on CAD data.
For most low-volume projects, tooling costs typically range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, making injection molding without high tooling costs achievable for startups and low-volume industrial parts.
Per-Part Cost
Per-part cost is influenced by multiple variables throughout the manufacturing process, including:
Material price and plastic pellets used
Cycle time on the injection molding machine
Labor and setup requirements
Post-processing and secondary operations
While the cost per molded part may be higher than in high-volume production, low-volume injection molding can significantly reduce total project cost. This is because tooling investment is lower, lead times are shorter, and production runs are aligned closely with actual demand.
As volumes increase, injection molding can also reduce cost per part, making it a scalable plastic manufacturing solution.
Design Changes and Revisions
Low-volume injection molding minimizes financial risk when design changes or revisions are required. Because bridge tooling solutions and aluminum molds are easier to modify, design updates can be implemented without rebuilding the entire tool.
This flexibility supports functional prototype molding, plastic part validation, and injection molding for testing and validation before committing to long-term volume production.
Low Volume Injection Molding vs Other Manufacturing Methods
Injection molding is one of several manufacturing methods available for producing plastic parts. However, its advantages become clear when compared to alternatives.
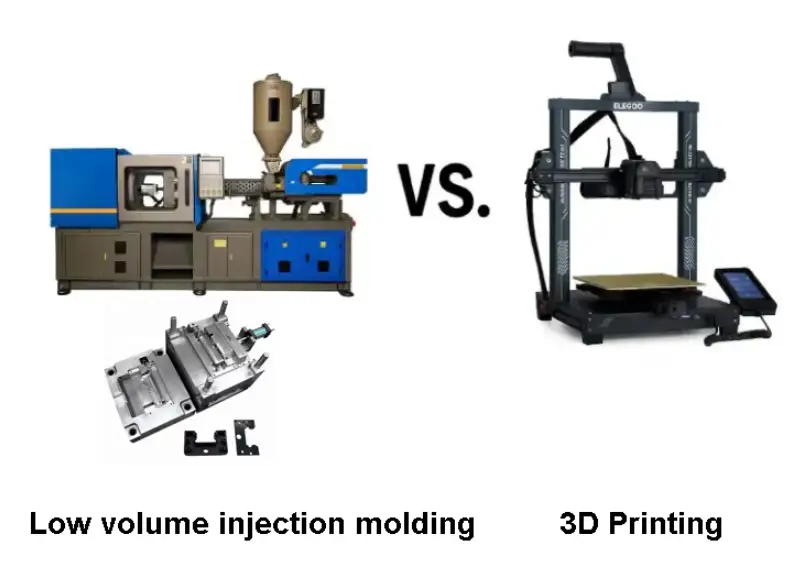
Low Volume Injection Molding vs 3D Printing
| Aspect | Injection Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Production-grade | Limited |
| Surface Finish | Excellent | Moderate |
| Per-Part Cost | Lower at scale | High |
| Tooling | Required | None |
Injection molding is a fast and reliable way to produce injection-molded prototype parts with real thermoplastics. Unlike 3D printed parts, injection molding to deliver production-grade prototype molding ensures consistent performance, better surface finish, and tighter tolerances for small parts and complex parts.
Low Volume Injection Molding vs Vacuum Casting
Compared to vacuum casting, injection molding provides better material consistency, tighter tolerance control, and higher repeatability. Molten plastic pellets are injected into a precision mold cavity, allowing injection molding applications to achieve parts with tight tolerances and stable dimensions across small-run production.
Low Volume vs High Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding focuses on flexibility, fast lead times, and lower upfront investment, while high-volume injection molding prioritizes cost per unit and long-term efficiency for mass production.
Low volume production molding services are ideal when production needs are uncertain or evolving, whereas high-volume production is best suited for stable, predictable demand.

Quality Control in Low Volume Injection Molding
Even small production runs require strict quality standards to ensure precision plastic molding and consistent results.
Inspection Methods
Dimensional inspection for tolerance verification
Visual inspection for surface finish quality
Functional testing for performance validation
Material certification to confirm thermoplastic properties
These steps ensure that each molded part meets design specifications and application requirements.
Process Control
Consistent injection molding machine parameters ensure repeatability across batches. Close monitoring of temperature, pressure, and cycle time allows injection molding to deliver reliable results even in low quantities or small batch production.
Design Tips for Low Volume Injection Molding
To maximize efficiency, reduce cost per part, and improve manufacturability:
Maintain uniform wall thickness
Avoid unnecessary undercuts
Use standard textures to reduce tooling cost
Design for easy ejection using ejector pins
Collaborate with the injection molder early
Early DFM collaboration helps optimize mold design, improve surface finish, and shorten lead times.
Choosing the Right Low Volume Injection Molding Supplier
Selecting the right partner is critical for achieving consistent quality and cost control.
Key Factors to Evaluate
Experience with low-volume injection molding projects
In-house tooling and mold manufacturing capability
Expertise in thermoplastics and material selection
Quality control systems and documentation
Clear communication and project management
A capable injection molder can support flexible manufacturing solutions from prototype to production.
Engineering Support
A good supplier provides Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback and engineering support. This helps refine CAD models, optimize mold cavity layout, and ensure injection molding can be used to produce plastic parts efficiently and reliably.


When Is Low Volume Injection Molding the Best Choice?
Low volume injection molding is ideal when:
Production quantities are limited
Product design is still evolving
Market demand is uncertain
Speed to market and short lead times are critical
Production-grade parts are required
In these scenarios, low-volume injection molding provides a cost-effective solution for meeting real-world production needs.
Future Trends in Low Volume Injection Molding
The industry continues to evolve through:
Faster CNC machining for tooling
Digital manufacturing workflows
Smart molds with sensors
Sustainable materials and recycling initiatives
These advancements further improve turnaround time, reduce production costs, and enhance flexibility for low-volume industrial parts.
Conclusion
Low volume injection molding is a powerful manufacturing solution that bridges the gap between prototyping and mass production. It enables companies to produce plastic parts with tight tolerances, excellent surface finish, and reliable material performance—without the high investment typically associated with volume production.
For startups, product developers, and manufacturers serving niche markets, low-volume injection molding provides a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to produce injection-molded parts with confidence.
By understanding tooling strategies, cost factors, quality control requirements, and supplier selection, businesses can fully leverage the benefits of low volume injection molding and bring products to market faster and more efficiently.
FAQ about low volume injection molding
What is low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce small quantities of plastic parts, typically between 50 and 10,000 units, using injection molds designed for short production runs.
How many parts qualify as low volume injection molding?
Low volume injection molding usually refers to production runs from a few dozen up to around 10,000 parts, depending on the material, mold type, and part complexity.
What are the main benefits of low volume injection molding?
Key benefits include lower tooling costs, faster lead times, production-grade part quality, design flexibility, and reduced risk compared to high-volume injection molding.
Is low volume injection molding suitable for end-use parts?
Yes, parts produced through low volume injection molding are made from real thermoplastics and are suitable for functional testing and final end-use applications.
What materials are commonly used in low volume injection molding?
Common materials include ABS, polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), nylon (PA), TPU, TPE, and high-performance plastics such as PEEK.
How much does low volume injection molding cost?
Costs vary based on part design, material selection, and tooling type. While per-part costs are higher than mass production, total project costs are much lower due to reduced tooling investment.
What type of tooling is used for low volume injection molding?
Aluminum molds, soft steel molds, and modular tooling systems are commonly used to reduce tooling cost and lead time.
How long does low volume injection molding take?
Tooling lead times are typically 2 to 4 weeks, with production completed shortly after mold approval, depending on project complexity.
How does low volume injection molding compare to 3D printing?
Low volume injection molding provides better material properties, tighter tolerances, and superior surface finish compared to most 3D printing methods.
Can design changes be made during low volume injection molding?
Yes, one of the main advantages is that molds can be modified more easily and at lower cost than hardened steel molds used for high-volume production.
What industries use low volume injection molding most often?
Industries such as medical devices, automotive, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, packaging, and startups commonly rely on low volume injection molding.
Is low volume injection molding a good option for startups?
Yes, it allows startups to validate designs, test the market, and launch products with lower upfront costs and minimal financial risk.
What tolerances can low volume injection molding achieve?
Tolerances are comparable to standard injection molding, typically around ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm, depending on part geometry and material.
When should low volume injection molding be chosen over high volume molding?
It is ideal when demand is limited, designs are still evolving, or bridge production is needed before scaling to mass manufacturing.
Can low volume injection molding be scaled to high volume production later?
Yes, designs proven through low volume injection molding can be transferred to hardened steel tooling for high-volume production with minimal changes.
Get a quote for low volume injection molding
Get a quote for low volume injection molding today and discover a reliable solution for producing high-quality, multi-material plastic components. Our experienced team supports custom design, material selection, DFM, mold flow analysis to ensure strength, precision, and cost-effective manufacturing for your low volume injection molding project.

