Prototype injection molding services
Custom prototype injection molding with AIM plastic, with design and engineering support, OEM, ODM, injection mold making, competitive price, shipment support
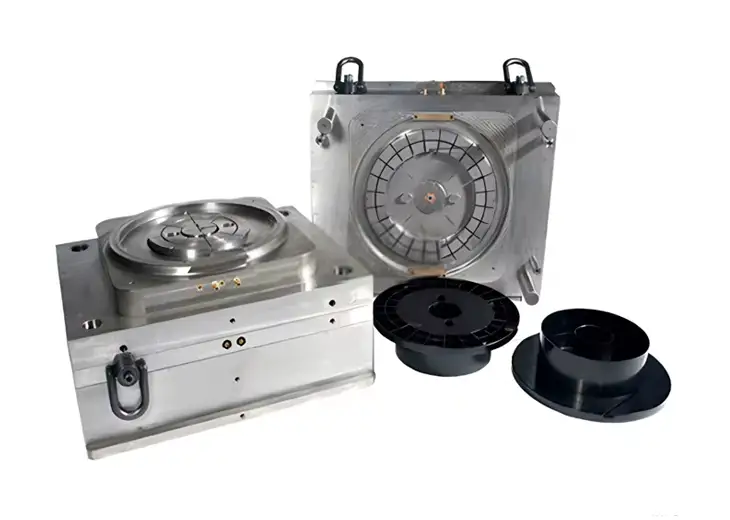

Prototype injection molding has become an essential process in modern product development as markets continue to demand faster innovation, shorter product life cycles, and higher performance standards. Traditional prototyping methods, such as basic 3D print models or CNC machining, are no longer sufficient for validating complex plastic components.
Prototype injection molding bridges the gap between early design validation and mass production by producing realistic, production-grade molded parts in a short timeframe.
Unlike additive manufacturing or subtractive processes, prototype injection molding relies on a real injection mold, professional tooling, and an industrial injection molding machine. This allows manufacturers to create injection molded parts using the same materials, mold structure, and injection molding process planned for full-scale production.
As a result, engineers can evaluate part performance under real-world conditions, including strength, fit, surface quality, and dimensional stability. This approach is especially valuable for identifying mold-related issues early. Factors such as material flow, cooling behavior, and part ejection can be tested before investing in hardened production tooling.
By using a prototype injection mold or prototype tool, design teams can make fast adjustments while keeping tooling costs under control. In some cases, 3D print technology is used to assist with mold inserts or auxiliary components to speed up rapid prototyping.
This guide explores what prototype injection molding is, how the process works, its advantages, applications, materials, tooling cost considerations, and how to select the right injection molding service for prototype projects.
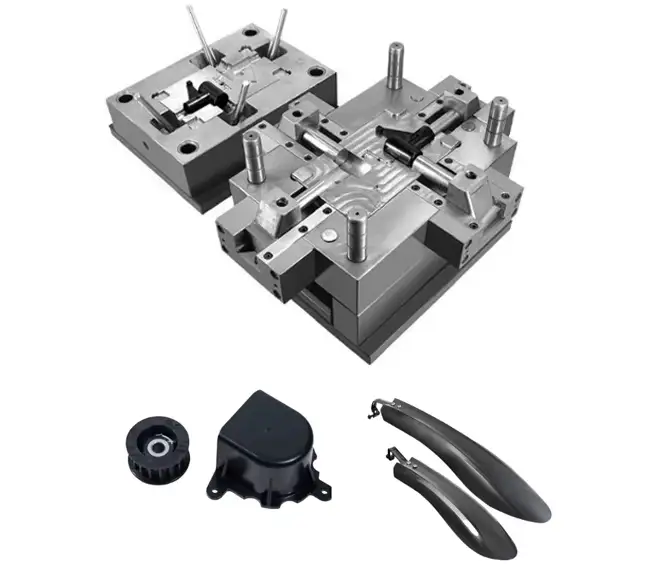

What Is Prototype Injection Molding?
Prototype injection molding is the process of manufacturing low-volume plastic parts using injection molding technology before full production begins. The primary goal is to validate part design, mold structure, material selection, and overall manufacturability using real injection conditions.
Unlike production molds built for long-term use, prototype molds are optimized for speed and flexibility. They are often made from aluminum or pre-hardened steel, which reduces both tooling costs and lead time. Prototype tooling is ideal for creating molded prototypes, conducting functional testing, and facilitating design iteration.
Prototype injection molding is commonly used for:
Design verification and optimization
Functional and mechanical testing
Market testing and early user feedback
Low-volume production molding
Pilot runs and pre-production validation
With rapid prototyping injection molding, and quick turn injection molding services, manufacturers can refine prototype plastic parts efficiently and move confidently toward mass production.
Why Prototype Injection Molding Is Critical in Product Development
1. Early Detection of Design Issues
Plastic injection molding introduces a wide range of manufacturing challenges, including shrinkage, warpage, sink marks, and flow imbalance. These issues are often invisible during early concept stages but become costly during full-scale production. Prototype injection molding allows manufacturers to evaluate part design, mold design, and overall manufacturability before committing to production tooling.
By using a real prototype mold—often built with aluminum prototype tooling or simplified prototype mold design—engineers can observe how injection molding materials behave inside the cavity. This early feedback enables design adjustments while the prototype molds cost remains manageable, preventing expensive rework of production injection molds later in the product development cycle.
2. Real Material Performance Testing
Unlike alternative prototyping approaches that rely on substitute plastics or simulated properties, prototype injection molding uses the same injection molding materials planned for mass production. This ensures that prototype injection-molded components accurately reflect final performance.
Manufacturers can test strength, heat resistance, chemical exposure, and surface finish on functional prototype parts under real molding conditions. Whether producing custom prototype molding samples or low-volume prototype parts, this approach provides reliable data for prototype and production alignment, reducing uncertainty before a production run begins.
3. Faster Time to Market
Speed is a major advantage of rapid injection molding. Modern prototype injection molding services can deliver prototype molds in weeks rather than months, significantly reducing lead times compared to traditional production tooling.
Advanced techniques such as 3D printed molds, a 3D printed injection mold, or even a silicone mold prototype can be integrated into the prototype manufacturing process to accelerate early molding projects. Faster tooling enables quicker design iterations, allowing injection molding projects to move efficiently from prototype parts to production injection molds.
4. Reduced Financial Risk
Validating an injection molding project with prototype injection molding dramatically lowers financial risk. By confirming part design, mold behavior, and material selection early, companies avoid costly mistakes during full-scale production.
Testing injection-molded components before investing in hardened production tooling ensures smoother scaling from prototype and production stages, protecting budgets and timelines.
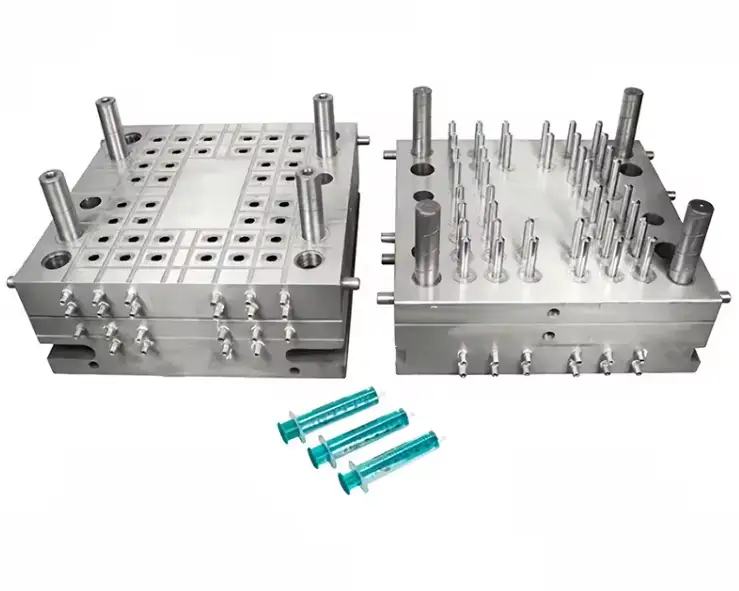
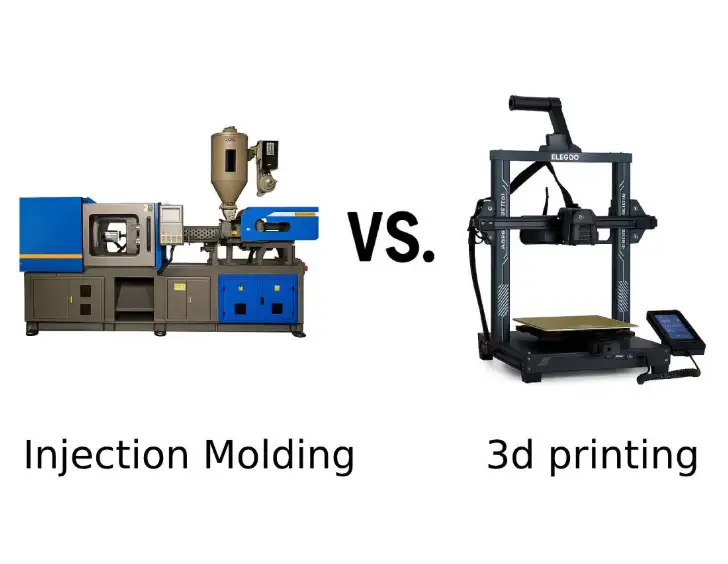
Prototype Injection Molding vs Other Prototyping Methods
Prototype Injection Molding vs 3D Printing
3D printing is useful for visual models and early concept validation, but it cannot replicate real plastic injection molding conditions. Even advanced 3D printed injection mold solutions have limitations in durability and material behavior.
Prototype injection molding provides:
Production-grade plastic materials
Consistent part dimensions
Accurate surface finishes
Real mold filling and cooling behavior
Prototype Injection Molding vs CNC Machining
CNC machining delivers precision but struggles with complex internal geometries common in injection molded components. Machined plastic parts also fail to represent real mold flow, cooling patterns, and part ejection behavior.
Prototype injection molding produces prototype injection molded components that closely match final production parts, ensuring a reliable transition into production tooling and full-scale manufacturing.
The Prototype Injection Molding Process
1. Design Review and DFM Analysis
The prototype injection molding process begins with a detailed review of 3D CAD data. Engineers evaluate part geometry and conduct Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis to ensure the design is suitable for real molding applications. Key factors such as wall thickness consistency, draft angles, undercuts, gate locations, and cooling efficiency are carefully examined.
At this stage, mold flow analysis for prototypes is often performed to predict how molten plastic will behave inside the cavity. This helps identify potential issues related to filling, air traps, weld lines, or shrinkage before any initial tooling is created. Early material selection is also addressed to confirm that prototype injection molding materials match the intended end-use requirements.
2. Mold Design
Once the design is validated, the prototype mold design begins. Prototype molds are intentionally simplified to reduce tooling cost and lead time while still supporting functional testing.
Common design characteristics include:
Single-cavity or low-cavity configurations
Simplified runner and gating systems
Standardized mold bases
Manual or semi-automatic ejection mechanisms
This approach allows injection molding tooling to be produced quickly while still delivering reliable data for injection molding prototypes' benefits, such as realistic part quality and repeatability.
3. Mold Manufacturing
After mold design approval, mold manufacturing begins. Prototype molds are commonly produced using aluminum or pre-hardened steel, depending on durability requirements and production volume. CNC machining and EDM processes are widely used to manufacture mold components with sufficient accuracy for prototyping processes.
These methods ensure the initial tooling can withstand repeated cycles on an injection molding machine while maintaining dimensional stability for prototype part testing and evaluation.
4. Trial Molding and Sampling
With the mold installed on the molding machine, trial runs begin. During this phase, injection molding produces a set of initial prototypes for evaluation.
Engineers assess key criteria, including:
Dimensional accuracy
Surface appearance and finish
Material performance
Assembly and functional fit
These early samples are essential for validating both the prototype injection molding materials and the overall molding behavior under real processing conditions.
5. Iteration and Optimization
One of the core advantages of prototype injection molding services is the ability to iterate quickly. Feedback from initial prototypes often leads to refinements in part geometry, mold features, or processing parameters. Design changes can be implemented efficiently, allowing multiple optimization cycles before committing to production tooling.
This rapid iteration process ensures smoother transitions from prototyping to full production and supports a wide range of molding applications across different industries.
Materials Used in Prototype Injection Molding
One of the key advantages of prototype injection molding is material flexibility throughout the product development process. Because injection molding enables the use of real, production-grade plastics, manufacturers can evaluate part performance under realistic conditions.
Unlike prototyping methods that do not require tooling, plastic injection molding does require tooling and mold preparation, which makes testing more accurate and scalable.
Common thermoplastic molding materials include:
ABS – Tough, impact-resistant, and cost-effective for functional prototype parts
Polypropylene (PP) – Lightweight and chemically resistant, suitable for durable applications
Polyethylene (PE) – Flexible and impact-resistant for molded components
Polycarbonate (PC) – High strength with excellent transparency
Nylon (PA) – Strong mechanical properties and good wear resistance
TPE / TPU – Flexible, rubber-like materials for soft-touch parts
POM (Acetal) – Low friction and high dimensional stability
During the injection molding process, molten plastic is injected into molds made from aluminum or steel. In early-stage projects, 3D printed mold inserts may be used to reduce lead time and tooling cost. Although prototype injection molding does require tooling investment, it allows realistic per-part evaluation, accurate cost per unit estimation, and smooth scaling toward thousands of parts.
Using real injection molding materials ensures reliable performance data and supports informed decisions for full production.
Types of Prototype Injection Molds
Aluminum Prototype Molds
Aluminum prototype molds are widely used in rapid prototyping processes due to their fast machining time, lower per-part cost, and suitability for plastic prototype production. Molds are typically designed for hundreds to thousands of parts with precision, making them ideal for testing plastic part geometry and functionality early in the product development process.
Aluminum molds can be quickly fabricated and are compatible with standard injection molding machines, enabling rapid tooling solutions and quick injection molding quotes for fast project turnaround.
Soft Steel Prototype Molds
Soft steel prototype molds offer greater durability than aluminum and are often used for bridge tooling or pilot production. These molds allow more shots and a closer simulation of production molds, which makes prototype part iteration more accurate.
Injection molding also supports functional testing of plastic components under real production conditions, providing reliable performance data before final production tooling is committed.
Bridge Molds
Bridge molds serve as an intermediate solution between prototype and full production molds. They are commonly applied for low- to medium-volume production while full-scale production tooling is being prepared. Bridge tooling enables rapid production of parts with precision while maintaining flexibility for design adjustments identified through prototype part testing.

Applications of Prototype Injection Molding
Prototype injection molding is used across various industries, supporting both functional testing and visual validation.
Common applications include:
Automotive – Interior components, clips, fasteners, and functional housings
Medical – Device housings, disposable components, and testing parts
Consumer Electronics – Enclosures, structural components, buttons, and connectors
Industrial Equipment – Mechanical parts, covers, and protective components
Consumer Products – Packaging, household items, and lifestyle products
Injection molding prototyping offers the advantage of producing production-like plastic parts for early validation, ensuring accurate design for manufacturability and performance.
Lead Time for Prototype Injection Molding
Prototype mold lead time varies depending on part complexity, material selection, and tooling method. Typical timelines include:
Mold design: 3–7 days (often supported by digital prototyping molding, or 3D printer-assisted inserts)
Mold manufacturing/fabrication: 7–21 days
Sampling and prototype part iteration: 3–10 days
Using rapid tooling solutions, functional injection-molded prototypes can often be delivered within 2–4 weeks. By combining fast fabrication, standard injection molding techniques, and flexible prototyping methods, manufacturers can accelerate plastic prototype production while maintaining cost-effectiveness and high-quality results.
Cost of Prototype Injection Molding
The cost of prototype injection molding depends on multiple factors, including part size, complexity, cavity count, mold material, plastic selection, and required quantity. While prototype molds cost more than simple 3D printed parts, they are far less expensive than full production molds and provide high-quality, production-relevant validation data.
Using injection molding for prototypes allows designers to test engineering prototype parts under realistic conditions, including actual cycle time, surface finish, and dimensional tolerances, which helps ensure success in full-scale manufacturing.
High precision prototyping with CNC-machined prototype molds enables accurate evaluation of critical features and functional performance. This is particularly important in industries such as medical device manufacturing, consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial equipment, where injection-molded prototypes must meet strict quality standards.
Rapid injection molding benefits include faster iterations, early detection of part defects, and realistic testing of injection-molded components using production-quality plastics.
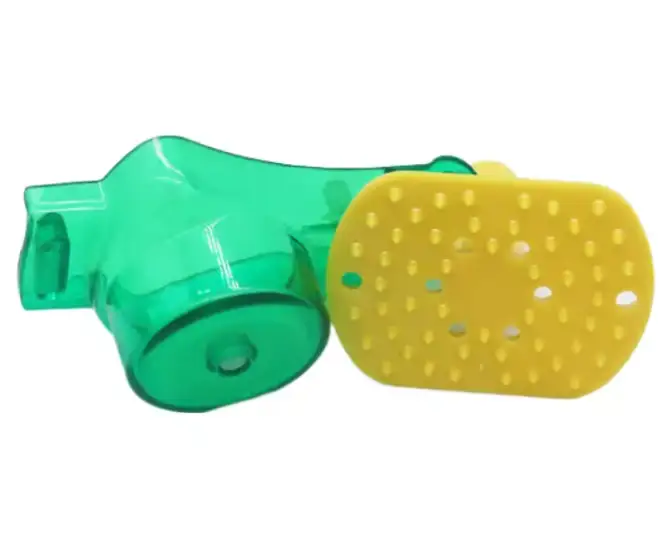

Design Tips for Successful Prototype Injection Molding
To maximize the value of prototype molding and reduce the cost of the tool, follow these prototype injection molding tips:
Maintain uniform wall thickness to ensure even material flow and reduce sink marks
Include proper draft angles for easy ejection from the mold
Minimize unnecessary undercuts to simplify the mold and reduce cavity complexity
Select prototype material selection that reflects actual production plastics
Design with future production in mind to reduce rework when moving from prototype vs production molding
Good design decisions during the prototyping process help improve prototype injection molding quality, optimize cycle time, and minimize downstream costs.
Choosing the Right Prototype Injection Molding Supplier
A reliable prototype molding supplier should provide:
Comprehensive design for manufacturability (DFM) and engineering support
In-house mold fabrication, including CNC machining for high-precision cavities
Guidance on injection molding materials for both prototype and production parts
Quick turn capabilities and rapid injection molding technologies to meet tight timelines
Clear communication during the prototype part iteration and the prototype molding process steps
The right partner can help accelerate prototype product development while ensuring injection-molded prototypes closely match production-quality parts.
Prototype Injection Molding vs Production Injection Molding
While both prototype and production injection molding use similar technology, their objectives differ:
Prototype molding focuses on:
Speed and quick turn capability
Flexibility for design changes
Validation of part design and functional performance
Production molding focuses on:
Efficiency and consistent cycle time
Long-term tool durability
High-volume consistency and production-quality finishes
Prototype injection molding is an essential step in reducing risk, verifying designs, and ensuring a smooth transition to full-scale manufacturing.
By using injection-molded prototypes, companies across various industries can optimize part performance, refine mold design, and make informed decisions before committing to expensive production molds. This approach ensures high-quality, functional parts while supporting cost-effective, rapid development.
Common Challenges in Prototype Injection Molding
Balancing speed with precision
Rapid prototyping and prototype tooling turnaround must deliver parts quickly while maintaining prototype molding finishes and tight prototype molding tolerances. Achieving both speed and accuracy can be challenging, especially for small-batch injection molding.Managing design changes efficiently
Prototype injection runs often reveal issues in part geometry or functionality. Prototyping is the process of iterating on designs before committing to full-scale production, but frequent changes can complicate workflow and require careful planning.Controlling cost while maintaining quality
Low-cost prototype molding must still justify the expense of CNC-machined molds and prototype tooling. Prototype mold maintenance and prototype mold testing are essential to avoid costly rework while producing high-quality, production-relevant parts.Simulating production conditions accurately
Unlike simpler methods like 3D printing, injection-molded prototypes replicate cycle time, molten plastic flow, and part ejection under realistic conditions. Ensuring the mold is designed correctly and performing prototype mold testing helps replicate production-quality parts.
Working with experienced engineers and following the design for manufacturability prototypes can help overcome these prototype molding challenges.
Future Trends in Prototype Injection Molding
Faster CNC machining and automation
Advances in CNC and digital prototyping molding reduce prototype mold lead time and support rapid injection molding benefits.Improved mold materials
New aluminum alloys and harder steels extend mold life and allow difficult-to-machine designs to be tested with low-cost prototype molding.Integration with digital simulation tools
Software for mold flow analysis and digital prototyping allows teams to iterate efficiently, produce parts with precision, and evaluate prototype molding tolerances before committing to expensive production molds.Increased use of bridge tooling in injection molding
Bridge molds support small batch injection molding and prototype injection runs while full-scale production molds are being prepared, ensuring a smooth prototype to production transition.
These trends make prototype injection molding an increasingly valuable tool in agile manufacturing, enabling quick turn prototypes, functional testing, and high-quality surface finishes.
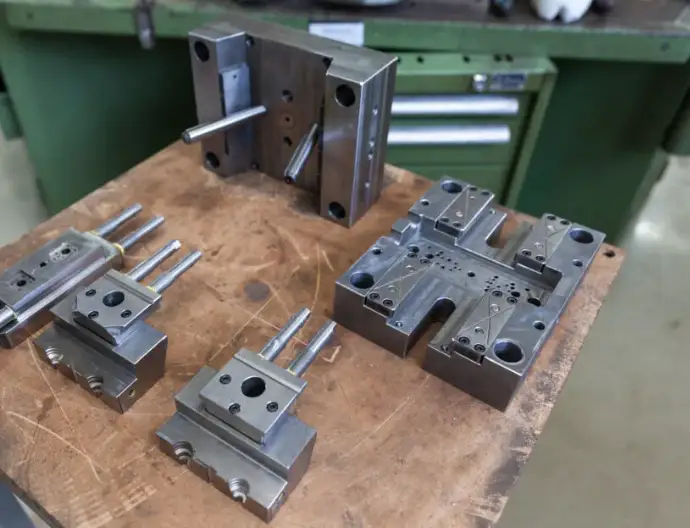

Conclusion
Prototype injection molding is a strategic necessity in modern product development. By producing real injection-molded plastic parts using production materials, manufacturers can validate designs, optimize performance, and make informed decisions before committing to full-scale manufacturing.
Prototyping is the process that allows evaluation of design before committing to expensive production molds, minimizes risk, and supports a smooth prototype to production transition.
With bridge tooling injection molding, low-cost prototype molding, and careful prototype mold maintenance, companies across various industries can achieve faster time to market, improved prototype injection molding quality, and reduced development risk.
Prototype injection molding remains the best way to avoid costly mistakes while ensuring functional, high-quality parts for full-scale production.
FAQ about prototype injection molding
1. What is prototype injection molding?
Prototype injection molding is the process of producing low-volume, functional plastic parts using real molds and production-grade materials. It allows engineers to test designs before committing to full-scale manufacturing and ensures accurate prototype injection molded components.
2. How does prototype injection molding differ from 3D printing?
Unlike 3D printing, which is ideal for early conceptual models, prototype injection molding produces parts with production-quality surface finish, accurate molding tolerances, and realistic material properties for functional testing.
3. What materials are used in prototype injection molding?
Common materials include ABS, polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polycarbonate (PC), nylon (PA), TPE/TPU, and POM. Using production-grade plastics ensures that prototype parts reflect final performance.
4. What are the benefits of prototype injection molding?
Prototype injection molding supports rapid prototype part iteration, functional testing, and design for manufacturability prototypes. It reduces risk, provides reliable data, and helps accelerate prototype to production transition.
5. How long does it take to produce a prototype mold?
Prototype mold lead time varies depending on complexity, material, and tooling method. Aluminum molds are typically faster, taking 1–3 weeks, while soft steel or bridge tooling molds may require slightly longer.
6. What industries use prototype injection molding?
Prototype injection molding is used across various industries, including automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and consumer products.
7. How many parts can a prototype mold produce?
Aluminum prototype molds can produce hundreds to thousands of parts, while soft steel and bridge molds can support higher quantities with precision.
8. Can prototype molds simulate full-scale production conditions?
Yes. Prototype injection molding replicates cycle time, molten plastic flow, part ejection, and prototype molding finishes similar to production molds, providing accurate performance validation.
9. What is the cost of prototype injection molding?
Costs depend on part size, complexity, number of cavities, mold material, and plastic selection. Prototype molds are significantly less expensive than production molds but justify the expense by delivering reliable prototype plastic injection data.
10. What are the main challenges of prototype injection molding?
Prototype molding challenges include balancing speed with precision, managing design changes efficiently, controlling cost while maintaining quality, and ensuring accurate simulation of production conditions.
11. How is CNC machining used in prototype molding?
CNC machining is commonly used to fabricate mold components, create precise cavities, and produce functional prototype parts that accurately reflect production-quality performance.
12. What is bridge tooling in prototype injection molding?
Bridge tooling injection molding is an intermediate solution for low- to medium-volume production while final production molds are being prepared. It supports small batch injection molding and prototype injection runs.
13. Can prototype injection molding help reduce production risk?
Yes. It allows engineers to validate design for manufacturability, test material selection, and refine mold design before committing to expensive production molds.
14. What is rapid injection molding?
Rapid injection molding is a fast and cost-effective method to produce functional prototype parts quickly. It often uses aluminum prototype tooling or 3D printed mold inserts to accelerate the prototype manufacturing process.
15. How does prototype injection molding support product development?
Prototype injection molding accelerates the product development process by delivering functional, high-quality parts, validating designs, optimizing mold features, and enabling a smooth transition from prototype to full-scale production.
Get a quote for your prototype injection molding
Get a quote for your prototype injection molding today and discover a reliable solution for producing high-quality, multi-material components. Our experienced team supports custom design, material selection, and scalable production to ensure strength, precision, and cost-effective manufacturing for your prototype injection molding project.

